Remote proctoring tests are gaining traction in educational institutions, and there are interesting facets that many may not know. For instance, diverse methods like live and automated proctoring play crucial roles in maintaining exam integrity. Identity verification uses facial recognition and multi-factor authentication to confirm the test-taker’s identity. Moreover, these systems aim for accessibility by accommodating various student needs, which is essential for creating an equitable testing environment. Automation also lightens the instructor’s workload by efficiently flagging suspicious behaviors, allowing them to focus more on teaching. Looking ahead, AI advancements will continue to enhance security during remote tests, reshaping the landscape of exam integrity further.
1. Diverse Proctoring Methods Explained
Remote proctoring test use different methods to ensure exam integrity. One main approach is live proctoring, where trained professionals supervise students in real-time through video feeds. This method allows for immediate intervention if something seems off. On the other hand, automated proctoring relies on artificial intelligence to monitor students’ behavior during the exam. AI can track actions like looking away from the screen or using unauthorized devices, flagging these behaviors for review. Some institutions prefer a hybrid model that combines both live and automated techniques, offering more flexibility while tightening security. For instance, a student might be monitored by an AI system, but a live proctor could step in if the AI flags any irregularities. Many proctoring platforms also include browser lockdown features, preventing students from accessing unapproved materials. However, the choice of method can vary between institutions based on their unique needs and resources. Some students may feel more at ease with one approach than another, impacting their performance. With continuous advancements in technology, we can expect even more refined proctoring methods in the future.
 2. Identity Verification Techniques in Remote Testing
2. Identity Verification Techniques in Remote Testing
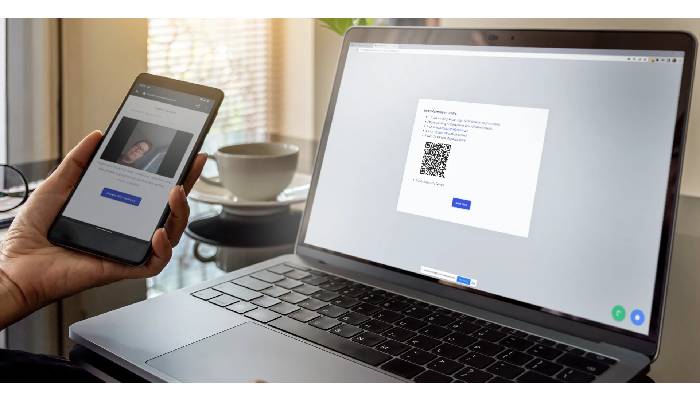
Identity verification is a crucial part of remote proctoring tests. It helps ensure that the person taking the exam is indeed the registered candidate. One common method used is facial recognition technology, where the test-taker’s live image is compared with a photo ID to confirm their identity. To add another layer of security, many platforms implement multi-factor authentication, requiring additional forms of identity confirmation, such as a one-time code sent to the test-taker’s phone.
Some innovative solutions are even exploring biometric measures, like fingerprint scanning, to enhance identity verification. Before starting an exam, students may be asked to take photos of both their ID and themselves, ensuring that the identities match up. Privacy concerns are taken seriously, with strict protocols in place to securely store biometric data and use it solely for verification purposes. Educational institutions must also comply with regulations regarding data protection and student privacy, ensuring that personal information is handled responsibly.
Real-time monitoring plays a vital role as well, helping to confirm that the individual who started the test remains the same throughout the duration of the exam. Ongoing advancements in technology are leading to more accurate and reliable identity verification methods, significantly reducing the chances of impersonation. Looking ahead, we can expect even more sophisticated techniques to emerge, further enhancing the security of remote testing.
- Identity verification is essential to ensure the correct individual is taking the test.
- Common methods include facial recognition, where the test-taker’s live image is matched with a photo ID.
- Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional forms of identity confirmation.
- Some platforms are exploring biometric measures, such as fingerprint scanning, to enhance identity verification.
- Verification processes often require students to take photos of their ID and themselves before starting an exam.
- Privacy concerns are addressed by ensuring that biometric data is securely stored and used only for verification.
- Institutions are required to comply with regulations regarding data protection and student privacy.
- Real-time monitoring can help verify that the test-taker remains the same person throughout the exam.
- Technological advancements are leading to more accurate and reliable identity verification methods.
- The future may see the introduction of more sophisticated verification techniques, further reducing impersonation risks.
3. Adaptability and Accessibility for All Students
Remote proctoring systems are designed to be inclusive, catering to students with various needs, including those with disabilities. Features such as screen readers and adjustable time limits ensure equitable access. Moreover, the flexibility of remote scheduling alleviates stress, allowing students to take exams at times that suit them best. Many platforms also support multiple languages, which aids non-native speakers in navigating the examination process. Customization options enable students to adjust settings based on their individual requirements, creating a more personalized experience. Accessibility features are continuously improved based on student feedback and evolving needs, ensuring that no student is disadvantaged due to a lack of access to technology or resources. Some platforms provide practice tests to familiarize students with the exam process before the actual test, while training resources are available for both students and instructors to ensure everyone understands the system. Collaboration with disability services helps institutions develop better proctoring solutions, promoting a fair testing environment for all.
4. Impact on Instructor Workload with Automation
Automation in remote proctoring is a game changer for educators, significantly lightening their workload. With technology taking over the monitoring of exams, instructors can spend less time overseeing the testing process and more time engaging with their students. Automated systems flag suspicious behavior, allowing teachers to focus on teaching rather than managing. Additionally, these proctoring solutions provide analytics that offers insights into student performance and engagement, helping educators identify where students might need extra support. By generating reports automatically, these systems free up valuable time that instructors can redirect toward lesson planning and fostering student relationships. The efficiency gained through automation not only makes the exam process smoother but can also enhance overall teaching effectiveness. However, to maximize these benefits, training on the proctoring technology is crucial, and feedback from instructors can be instrumental in refining these systems to better meet educational goals.
5. The Future of Exam Integrity in the AI Era
The future of remote proctoring is closely tied to advancements in AI technology, which is proving to be a game changer in maintaining exam integrity. With enhanced monitoring capabilities, AI tools can analyze student behavior to spot unusual patterns that may indicate cheating or collusion. For example, behavior analysis can track eye movements and detect if a student is looking away too frequently, which might suggest they are consulting unauthorized materials. Additionally, innovations like Smart Voice Detection are emerging, designed to monitor audio input during exams to prevent students from receiving outside help.
Machine learning algorithms are also becoming more sophisticated, improving the accuracy of detecting cheating over time as they learn from new data. This continuous evolution is crucial, especially as students develop new tactics to bypass proctoring measures. Future solutions may even incorporate virtual reality, creating immersive testing environments that enhance security while providing an engaging experience for students.
However, as technology evolves, ethical considerations regarding student privacy and data security must remain a priority. Collaboration between technology developers and educational institutions will be essential in shaping proctoring solutions that not only secure exams but also respect students’ rights. As emerging technologies continue to redefine the landscape of remote proctoring, the emphasis on exam integrity will become increasingly robust.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does remote proctoring actually work?
Remote proctoring uses special software to monitor you during a test, often through your webcam and microphone, to ensure you follow the rules.
Can I use my own computer for remote proctoring tests?
Yes, you can typically use your own computer, but it needs to meet specific technical requirements to run the proctoring software.
What kind of identification will I need for a remote proctoring test?
Usually, you will need to show an official form of ID, like a driver’s license or passport, to verify your identity before the test starts.
Is my privacy protected during remote proctoring?
Yes, most remote proctoring services have strict privacy policies in place to protect your personal information and test records.
What happens if I have technical issues during the test?
If you encounter technical problems during the test, you should notify the proctor immediately, as they can assist you in resolving the issue.
TL;DR Discover five lesser-known aspects of remote proctoring tests. Learn about the variety of proctoring methods, including live and automated options, and how identity verification techniques safeguard exam integrity. Explore how these systems promote accessibility for all students and the impact of automation on instructor workload. Finally, consider the future of exam integrity as AI technologies continue to evolve.
 2. Identity Verification Techniques in Remote Testing
2. Identity Verification Techniques in Remote Testing